The Internet of Things (IoT) can deliver a level of real-time surveillance and monitoring never seen in the industry before.
Big Data can unlock a “gold mine” of information that can help businesses predict different outcomes by evaluating business decisions as well as allowing them to explore new opportunities and eliminate those inefficiencies for decades.
In this article, we will briefly explain each technology as well as its potential in the industry. Then we will envision how the combination of the two technologies can be a profound breakthrough between logistics organizations and supply chains.
Big Data in Logistics.
What is Big Data?
Big Data refers to the process of analyzing large and complex data with sophisticated, predictive and behavioral methods to predict the likelihood of results.
Standard business reports focus on specific activities and parts. Big Data provides a holistic view of all of this data (and more) and tries to find its implications for developing models and predicting the likelihood of events that may happen in the future. .
The implications of Big Data in supply chain management
As more and more systems and devices are linked together, more and more data is created and collected in a single day. A study conducted by IDC shows that the amount of data will double every two years and will reach 44 zettabytes, or 44 trillion gigabytes in 2020.
The rapid growth of data is no stranger to the logistics and supply chain industries.
Historically, people working in the supply chain have created a vast amount of diverse and rich information. Everything from routes, carriers, delivery times, modes of transport, pricing points, sales, earnings and profits has been collected and stored in a database of multiple sales. Karma.
So how can Big Data impact the industry? Let’s go through an example
A company may want to know which modes of transport and shipping lines can be used to maximize profits for a particular destination while still meeting delivery times. Big Data can do this.
Or a line of ships wants to find out how during a particular time, during a certain season of the year, arriving at a particular location, weather conditions, can affect delivery times. Big Data can do it.
Using Big Data in supply chain management can help businesses more accurately forecast demand, better understand customer buying cycles, and calculate future stock output based on old data. .
With such a large amount and variety of data on the databases of many businesses, it is only a matter of time until companies start mining this “gold mine”.
Big Data has played a key role in Amazon’s success. The company has been harnessing data from more than 152 million (and increasingly) customers to understand purchase behavior and recommend products based on their purchase history and related products.
Data cannot be just considered information sitting on the cloud, but must be seen as a special asset to the organization. A “gold mine”.
IoT in Logistics
What is IoT?
The Internet of Things in logistics is a theme that is illuminating the imaginations of tech enthusiasts and visionary leaders in the supply chain.
The Internet of Things is the connection of devices and physical objects to sensors, allowing continuous recording of information about their state (location, temperature, movement, impact, etc.) tell location and time.
Advances in networking technology (Bluetooth, 4G, LTE, fiber-optic, etc.) available and low-cost, the ability to connect devices and sensors through and to a common point has never been possible. hours.
What impact can IoT have in Logistics industry?
While the availability and cost of sensors and networks can make the IoT evolve, battery life and lack of IoT standards remain among the final hurdles to overcome.
As vendors and solution providers overcome these challenges, this technology has the potential to bring supply chains and logistics industries into a new era.
An era where companies will be able to track any object or device that could keep a sensor in real time or hidden (by recording information that could later be downloaded in a system).
From boxes to pallets, trucks and containers, to people and more, anything that can hold a sensor can generate status-recording information.
The ability to record information in real time will allow businesses to respond to incidents and requests almost immediately and understand why, when planning, and how this happened. This will help them revise inefficiencies that may have been around for decades, deliver outstanding service, and minimize safety and security risks.
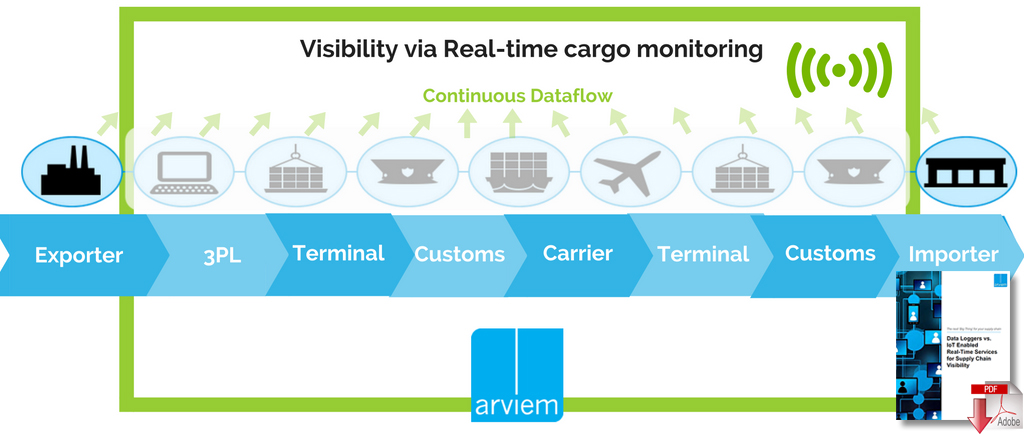
But it’s also a byproduct that is derived from all the interconnections of everything: lots of data! A lot of data is the raw material for Big Data and smarter, more strategic decisions.
The IoT in Logistics could represent a major change in the industry as it can provide companies with untapped opportunities to understand cause and effect. The ability for companies to evaluate different potential decisions and predict possible outcomes. It is almost a science for risk and business management.
IoT and Big Data in logistics can change the game.
As we have seen, each technology can benefit businesses and participants in the supply chain, but great benefits come from the combination of the two.
The IoT in logistics will bring the interconnection of devices, sensors, and systems that increase the volume, speed, and diversity of data. On the other hand, Big Data provides the ability to analyze available information and predict possible scenarios and outcomes.
Businesses that have the ability to incorporate these technologies will transition from a service-centric to information-focused organization.
An enterprise can make decisions based on the accuracy and reliability of the volume of data. A business can accurately understand the relationship between weather conditions, shipping, mode of transport, productivity, delivery times, and profitability. Or you can avoid the fragmentation of too little or too much resources by tracking your warehouse, workforce, and transportation usage in real time to meet demand.
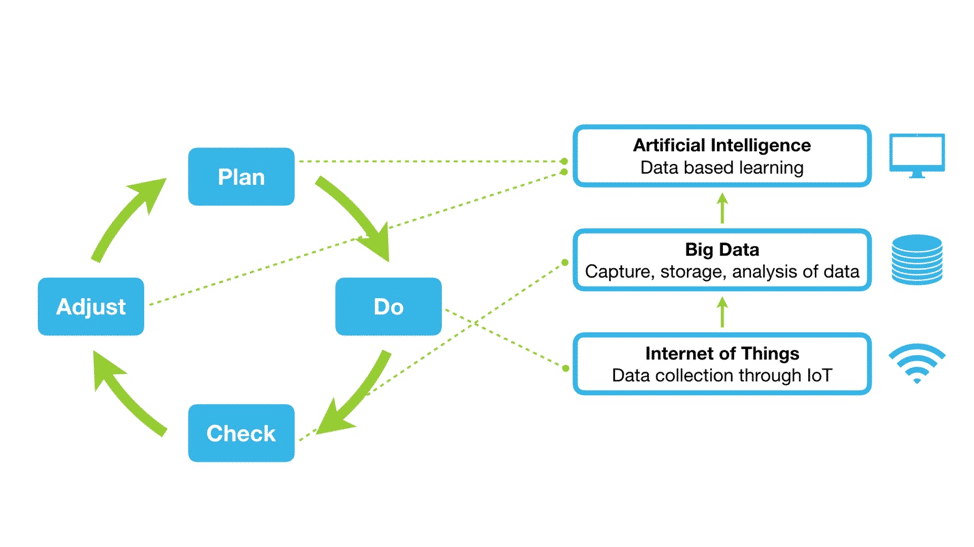
But it could be taken to another level.
Firms can understand the effects of changes in the behavior of certain market segments, changes in consumer consumption, the effects of financial policy, international trade and / or in GDP.
Businesses can envision investment possibilities and strategies in technology that will take a huge competitive edge when they can make better decisions, increase efficiency and exceed customer expectations.

